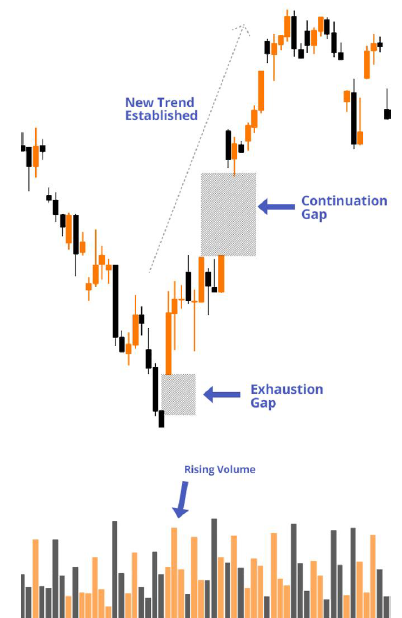
A Gap is when the price of a financial asset opens sharply above or below the previous day’s close with no trading activity in between.
The terms ‘gap up’ and ‘gap down’ refer to the direction of the price movement. A ‘gap up’ is when the opening price is higher than the previous day’s close price. Conversely, a ‘gap down’ is when the opening price is lower than the previous day’s close price.
Gaps can occur as a result of underlying fundamental factors. For example, the share price of a company may gap up the following day, if during after market hours, it reported better-than-expected earnings results.
Gaps can also occur as a result of technical factors. For example, if a company’s share price closes at all-time highs as a result of positive news throughout the day, it may ‘gap up’ or open at a higher price the following day if sentiment and momentum continue.